Understanding Injunctions in Legal Context
In India, an injunction is a legal remedy available to parties who wish to prevent the other party from carrying out a certain action or behavior. Injunctions can be granted in a variety of situations, such as in cases of intellectual property infringement, breach of contract, or defamation. An injunction is a powerful legal tool that acts as a court order requiring a party to do or cease doing specific actions. It plays a crucial role in many legal battles, serving as a preventive measure to stop legal wrongs or as a remedy to enforce rights. Understanding its dynamics, legal implications, and the scenarios where it applies is essential for both legal practitioners and those seeking legal relief.
Types of Injunctions in India:
- Temporary Injunctions – Temporary injunctions are granted to preserve the status quo until a final decision can be reached. These are usually granted at the start of a case and can last for the duration of the legal proceedings.
- Permanent Injunctions – Permanent injunctions are granted after the court has made a final determination in the case. They prohibit the defendant from continuing a particular action or behavior.
- Mandatory Injunctions – Mandatory injunctions require the defendant to carry out a particular action. They are often granted in cases of breach of contract, where the plaintiff requires the defendant to fulfill their contractual obligations.
- Prohibitory Injunctions – Prohibitory injunctions prohibit the defendant from carrying out a particular action or behavior. They are often granted in cases of intellectual property infringement or defamation.
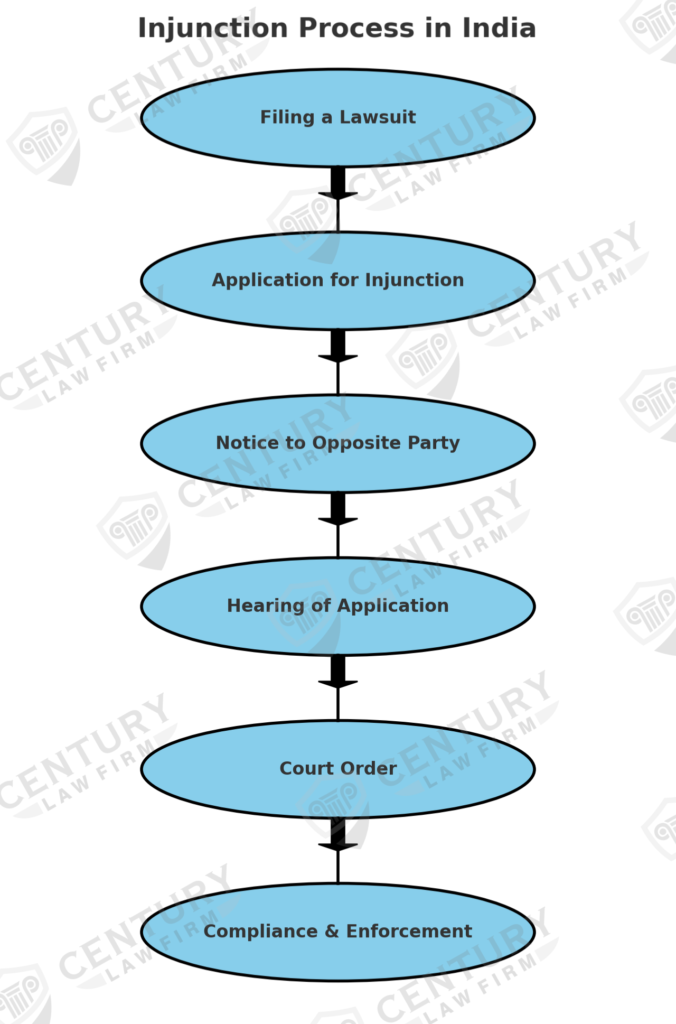
Procedure for obtaining an injunction in India:
- Filing of Suit: The first step in obtaining an injunction is to file a suit with the appropriate court. The suit should include all relevant facts and evidence, as well as a request for the injunction.
- Application for Temporary Injunction: If the plaintiff wishes to obtain a temporary injunction, they must file an application for the same along with the suit. The court may grant a temporary injunction if it deems it necessary to preserve the status quo until a final decision can be made.
- Notice to the Defendant: The court will issue notice to the defendant and give them an opportunity to respond to the application for the injunction.
- Hearing: The court will hear arguments from both parties and make a decision on whether or not to grant the injunction.
- Compliance with Injunction: If the court grants the injunction, the defendant must comply with it or face penalties such as fines or imprisonment.
Provision of Injunction in Indian Law
Under Indian law, injunctions are governed by the Specific Relief Act, 1963. The act provides for two types of injunctions – temporary injunctions and perpetual injunctions.
Section 37 of the Specific Relief Act deals with temporary injunctions. It states that a temporary injunction may be granted to the plaintiff to prevent the breach of an obligation or to prevent the commission of a wrongful act that would cause irreparable harm. The court may grant a temporary injunction if it is satisfied that the plaintiff has a prima facie case and that the balance of convenience is in favor of granting the injunction.
Section 38 of the act deals with perpetual injunctions. It states that a perpetual injunction may be granted to the plaintiff to prevent the breach of an obligation that is capable of specific performance or to prevent the commission of a wrongful act that would cause irreparable harm. The court may grant a perpetual injunction if it is satisfied that the plaintiff has a legal right to the property or to the relief sought, and that the defendant has acted in violation of the plaintiff’s legal right.
In addition to the Specific Relief Act, injunctions are also governed by the Civil Procedure Code, 1908. Section 94 of the code provides that a court may grant an injunction to prevent the breach of an obligation or to prevent the commission of a wrongful act that would cause irreparable harm. Section 95 of the code provides that a court may attach a property to ensure compliance with an injunction.
It’s important to note that injunctions are a discretionary remedy, and the court will consider various factors before deciding whether to grant an injunction. These factors may include the urgency of the matter, the balance of convenience, and the likelihood of success in the underlying lawsuit.
Order 39 of the Civil Procedure Code, 1908 deals with temporary injunctions and interlocutory orders. This order provides for the grant of temporary injunctions to maintain the status quo until the final disposal of the case. The provisions of Order 39 are meant to ensure that justice is served, and that parties are not subjected to irreparable harm before the final disposal of the case.
Section 37 of the Specific Relief Act, 1963 provides the substantive law for injunctions in India, while Order 39 of the Civil Procedure Code provides the procedural law. Under Order 39, temporary injunctions may be granted by the court either before or after the filing of a suit. The court may also grant an interim injunction while the suit is pending, to preserve the status quo until the final disposal of the case.
The provisions of Order 39 allow for the grant of different types of injunctions, such as prohibitory injunctions and mandatory injunctions. Prohibitory injunctions prohibit the defendant from carrying out a particular action or behavior, while mandatory injunctions require the defendant to carry out a particular action.
The provisions of Order 39 also provide for the issuance of ex parte injunctions, which are granted without giving notice to the defendant. An ex parte injunction may be granted in cases of urgency, where delay in granting the injunction would result in irreparable harm to the plaintiff.
It’s important to note that the grant of an injunction under Order 39 is a discretionary power of the court. The court will consider various factors before deciding whether to grant an injunction, such as the urgency of the matter, the balance of convenience, and the likelihood of success in the underlying lawsuit.
Strategies for Filing Effective Injunction Petitions
The success of an injunction petition largely hinges on how convincingly the petitioner can demonstrate the need for such an order. This involves clearly outlining the potential harm or irreparable damage that might occur without the court’s intervention. Additionally, understanding the legal criteria for each type of injunction and presenting strong, factual evidence to support the claim is key to a successful petition.
Case Studies: Injunctions in Action
Analyzing past injunction cases offers invaluable insights into how courts interpret and apply this legal provision. For instance, in cases of environmental protection, injunctions have been crucial in halting activities causing ecological damage. Similarly, in the corporate world, injunctions often play a role in intellectual property disputes, protecting proprietary information from unauthorized use or disclosure.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Order 39 of the Civil Procedure Code provides for the grant of temporary injunctions and interlocutory orders to maintain the status quo until the final disposal of the case. The provisions of this order allow for the grant of different types of injunctions, and also provide for the issuance of ex parte injunctions in cases of urgency. The grant of an injunction under Order 39 is a discretionary power of the court, and various factors will be considered before deciding whether to grant the injunction. injunctions are an important legal remedy in India, providing parties with a way to prevent the other party from carrying out a certain action or behavior. The provisions of the law governing injunctions include the Specific Relief Act, 1963, and the Civil Procedure Code, 1908. It’s important to seek the advice of a qualified legal professional before seeking an injunction, as the process can be complex and the consequences of non-compliance can be severe. injunctions are an important legal remedy in India, providing parties with a way to prevent the other party from carrying out a certain action or behavior. They can be granted in a variety of situations, and the procedure for obtaining an injunction involves filing a suit, applying for a temporary injunction, and attending a hearing. It is important for parties to seek the advice of a qualified legal professional before seeking an injunction, as the process can be complex and the consequences of non-compliance can be severe.
When choosing a lawyer, it’s important to consider their experience and qualifications in handling injunction cases. You may also want to consider their communication style, availability, and fees. It’s important to discuss these factors with the lawyer before hiring them to ensure that you are comfortable working with them and that they can meet your needs.
If you’re dealing with a legal dispute that requires a fast resolution, an injunction may be the solution you need. At Century Law Firm, we have extensive experience representing clients in injunction cases, both temporary and permanent.
Our team of experienced lawyers understands the complexities of obtaining injunction orders, and we have a track record of success in obtaining favorable results for our clients. We have represented clients in various matters, including property disputes, trademark and copyright infringement cases, and contractual disputes.
When you work with Century Law Firm, you can expect personalized attention from our team of experienced lawyers. We take a collaborative approach to legal representation, working closely with clients to understand their needs and goals and develop a customized legal strategy that meets their specific needs. We believe in open communication and keeping our clients informed throughout the legal process.
At Century Law Firm, we understand that legal issues can be expensive. That’s why we offer flexible fee structures and payment plans to make our services accessible to clients from all walks of life. Our goal is to provide high-quality legal services at a reasonable cost.
If you’re facing a legal issue that requires an injunction, we invite you to schedule a consultation with one of our experienced lawyers. We look forward to working with you to find a solution that meets your needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Injunction in India
- What is an injunction?
An injunction is a court order that requires a party to do or refrain from doing a certain act. Injunctions are often used to prevent harm or maintain the status quo until a legal dispute is resolved. - What are the types of injunctions?
Injunctions can be temporary or permanent. Temporary injunctions are issued to maintain the status quo until a legal dispute is resolved, while permanent injunctions are issued as part of the final judgment in a case. - When can I seek an injunction?
You can seek an injunction if you believe that another party’s actions are causing you harm or are likely to cause you harm. Injunctions are often sought in cases involving property disputes, trademark and copyright infringement cases, and contractual disputes. - How do I obtain an injunction?
To obtain an injunction, you need to file an application in court. You will need to demonstrate to the court that you are likely to suffer irreparable harm if the injunction is not granted. - How long does it take to obtain an injunction?
The time it takes to obtain an injunction can vary depending on the complexity of the case and the court’s schedule. Temporary injunctions can often be obtained quickly, while permanent injunctions may take longer. - What happens if the party violates the injunction?
If a party violates the injunction, they may be held in contempt of court and could face penalties such as fines or imprisonment. - Do I need a lawyer to seek an injunction?
It is highly recommended to seek the assistance of a qualified lawyer when seeking an injunction. A lawyer can provide guidance on the legal requirements for obtaining an injunction and can help you prepare and file your application in court. - What are the costs associated with seeking an injunction?
The costs associated with seeking an injunction can vary depending on the complexity of the case and the lawyer’s fees. It’s a good idea to discuss the costs with your lawyer before filing an application in court. - Can an injunction be appealed?
Yes, an injunction can be appealed if either party is dissatisfied with the decision. The appeals process may involve a higher court reviewing the case and making a new decision. - Is injunction also known as stay order?
Yes, an injunction is sometimes referred to as a stay order. Both injunctions and stay orders are court orders that prohibit or require certain actions by a party to a legal dispute. An injunction is a court order that requires a party to do or refrain from doing a certain act. Injunctions can be temporary or permanent, and they are often used to prevent harm or maintain the status quo until a legal dispute is resolved. A stay order, on the other hand, is a court order that suspends or postpones a legal proceeding. Stay orders can be issued for various reasons, such as to allow a party to appeal a decision or to allow time for settlement negotiations. In some cases, an injunction may be sought as part of a request for a stay order. For example, a party may seek an injunction to prevent another party from taking certain actions while a legal proceeding is stayed. It’s important to note that while injunctions and stay orders may have some similarities, they are different legal concepts with distinct requirements and effects. It’s always a good idea to consult with a qualified lawyer to understand your legal options and determine the best course of action for your specific situation. - What is the primary purpose of an injunction in legal disputes?
An injunction serves as a court order to prevent a party from performing certain actions or to mandate specific actions, often used to prevent irreparable harm. - Can an injunction be granted without a formal lawsuit?
Typically, an injunction is part of a larger legal action and requires filing a lawsuit. However, in urgent cases, courts may issue temporary injunctions before a full hearing. - How long does it take to obtain an injunction?
The time to obtain an injunction varies depending on the case’s urgency, complexity, and court schedules. Temporary injunctions can sometimes be obtained rapidly, while permanent injunctions may take longer. - Are injunctions applicable in family law cases?
Yes, injunctions are often used in family law, such as in cases of domestic violence, where they can order a party to refrain from certain actions. - What happens if someone violates an injunction order?
Violating an injunction order can lead to serious legal consequences, including contempt of court charges, fines, or even imprisonment. - Can an injunction be appealed?
Yes, parties can appeal an injunction. The appeal process typically involves a higher court reviewing the decision to grant or deny the injunction. - What factors do courts consider when granting an injunction?
Courts consider several factors, including the likelihood of irreparable harm without the injunction, the balance of hardships between parties, and the public interest. - Is it possible to get an injunction against a government body?
Obtaining an injunction against a government body is possible but can be more complex due to legal doctrines like sovereign immunity. - What is the difference between a temporary and permanent injunction?
A temporary injunction is a provisional remedy granted to maintain the status quo until a final decision is made, whereas a permanent injunction provides a long-term solution after the case’s merits are fully examined. - Are injunctions enforceable across different jurisdictions?
The enforceability of an injunction across jurisdictions varies and often depends on reciprocal arrangements or specific legal provisions between regions.
Also Read:
Understanding Article 13 of the Indian Constitution
Writ Petition – Types, Important Judgements, How and When to File | Lawyer for Writ Petition
Public Interest Litigation (PIL) in India | Best Lawyer for PIL



